State Values and Bellman Equation
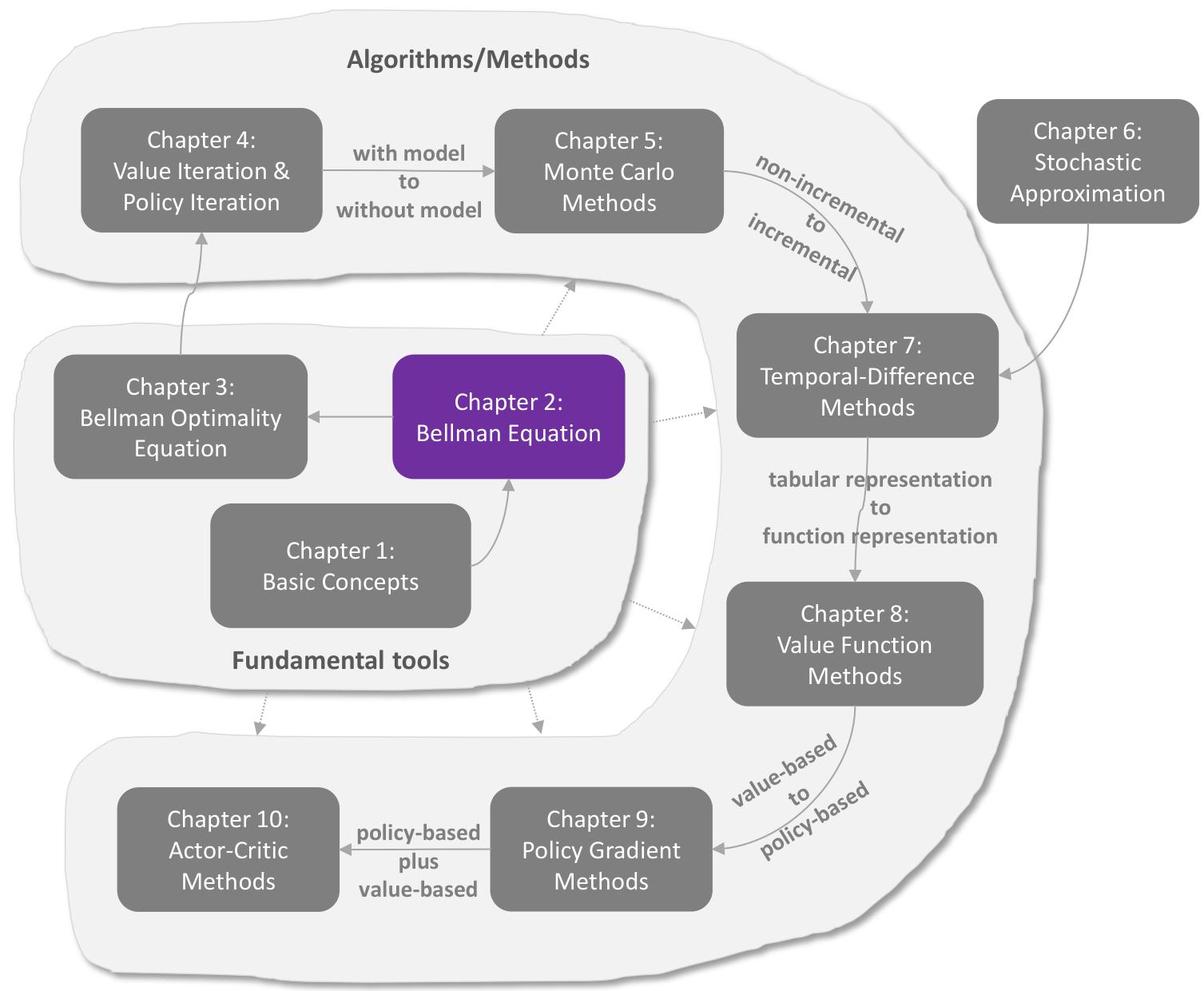
This chapter introduces a core concept and an important tool.
The core concept is the state value, which is defined as the average reward that an agent can obtain if it follows a given policy. The greater the state value is, the better the corresponding policy is. State values can be used as a metric to evaluate whether a policy is good or not. While state values are important, how can we analyze them?
The answer is the Bellman equation, which is an important tool for analyzing state values. In a nutshell, the Bellman equation describes the relationships between the values of all states. By solving the Bellman equation, we can obtain the state values. This process is called policy evaluation, which is a fundamental concept in reinforcement learning. Finally, this chapter introduces another important concept called the action value.
Sections
Motivating example
State values
Bellman Equation
Matrix-vector form of the Bellman equation
Solving state values from the Bellman equation
From state value to action value
Summary
The most important concept introduced in this chapter is the state value. Mathematically, a state value is the expected return that the agent can obtain by starting from a state. The values of different states are related to each other. That is, the value of state
Since state values can be used to evaluate whether a policy is good or not, the process of solving the state values of a policy from the Bellman equation is called policy evaluation. As we will see later in this book, policy evaluation is an important step in many reinforcement learning algorithms.
Another important concept, action value, was introduced to describe the value of taking one action at a state. As we will see later in this book, action values play a more direct role than state values when we attempt to find optimal policies. Finally, the Bellman equation is not restricted to the reinforcement learning field. Instead, it widely exists in many fields such as control theories and operation research. In different fields, the Bellman equation may have different expressions. In this book, the Bellman equation is studied under discrete Markov decision processes. More information about this topic can be found in [2].
Q&A
Q: What is the relationship between state values and returns?
A: The value of a state is the mean of the returns that can be obtained if the agent starts from that state.
Q: Why do we care about state values?
A: State values can be used to evaluate policies. In fact, optimal policies are defined based on state values. This point will become clearer in the next chapter.
Q: Why do we care about the Bellman equation?
A: The Bellman equation describes the relationships among the values of all states. It is the tool for analyzing state values.
Q: Why is the process of solving the Bellman equation called policy evaluation?
A: Solving the Bellman equation yields state values. Since state values can be used to evaluate a policy, solving the Bellman equation can be interpreted as evaluating the corresponding policy.
Q: Why do we need to study the matrix- vector form of the Bellman equation?
A: The Bellman equation refers to a set of linear equations established for all the states. To solve state values, we must put all the linear equations together. The matrix- vector form is a concise expression of these linear equations.
Q: What is the relationship between state values and action values?
A: On the one hand, a state value is the mean of the action values for that state. On the other hand, an action value relies on the values of the next states that the agent may transition to after taking the action.
Q: Why do we care about the values of the actions that a given policy cannot select?
A: Although a given policy cannot select some actions, this does not mean that these actions are not good. On the contrary, it is possible that the given policy is not good and misses the best action. To find better policies, we must keep exploring different actions even though some of them may not be selected by the given policy.